Student finance typically covers up to $10,000 annually for tuition, plus additional funds for living costs and materials, making higher education more accessible.
What is the maximum amount of student loans you can get?
The maximum amount of student finance loans you can borrow depends on the type of loan and your education level. For federal loans, undergraduates can borrow up to $57,500 in total (with no more than $23,000 in subsidized loans). Graduate or professional students can borrow up to $138,500 under the federal Direct Loan Program, which includes both undergraduate and graduate loans. Additionally, Parent PLUS Loans and Graduate PLUS Loans allow borrowing up to the full cost of attendance, minus any other financial aid received.
What is a normal student loan amount?
The average student finance loan debt for a borrower in the U.S. is around $30,000 to $40,000 for undergraduate degrees. This amount can vary widely depending on the type of school (public vs. private), location, and whether the borrower attends graduate school. Private student loans tend to increase the total debt, while those attending more affordable in-state public schools may have lower balances. Graduate and professional students can accumulate significantly higher debt levels, often exceeding $100,000.
How much in student loans should I take out?

You should only borrow as much in student finance loans as you absolutely need for tuition, books, and living costs. A good rule is to keep your total loan amount lower than what you expect to earn in your first year after graduation. This makes it easier to manage repayments later and helps you avoid taking on too much debt.
How much student finance do I have to pay back?
The amount of student finance you have to pay back depends on your income after you graduate. You only start repaying once you earn over a certain amount, and you pay a small percentage of your income above that threshold. If your income is below the limit, you don’t have to repay, and after a certain number of years, any remaining debt may be canceled.
Get a refund from student finance.
To request a refund from student finance, first contact your student finance provider to confirm eligibility and understand the process. You may need to fill out a refund request form or provide supporting documents. Ensure all required information is accurate and submit it through the prescribed method, whether online or by mail. Monitor your account or email for confirmation and updates on your refund status.
Do student loans affect credit scores?
Yes, student loans can affect credit scores. Timely payments can positively impact your credit by demonstrating good financial behavior, whereas missed or late payments can lower your score. The length of your credit history and your debt-to-income ratio, influenced by student loans, also play a role in determining your overall credit score.
How many people actually pay off their student loans?
The percentage of people who successfully pay off their student loans varies, but data suggests that around 40% of borrowers are able to repay their loans fully within 20 years. Many face challenges such as high interest rates, job instability, and repayment terms that extend beyond their initial expectations. Programs like income-driven repayment plans and forgiveness options aim to support those struggling to pay off their loans.
How Much Can You Borrow In Student Loans?
The amount you can borrow in student finance loans depends on several factors, including your year in school and dependency status. For federal Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans, undergraduate students can borrow up to $5,500 in the first year, $6,500 in the second year, and $7,500 in subsequent years, with a maximum total of $31,000. Graduate students can borrow up to $20,500 per year. Private loans may offer higher amounts, but terms vary by lender. For more details, please visit the website.
How Student Loans Are Used

Student finance loans are typically used to cover the cost of higher education, including tuition, fees, textbooks, and other related expenses. They can also help with living costs, such as housing and food, while attending school. These loans are repaid over time, often with interest, and can come from federal or private sources. Properly managing student loans is crucial for minimizing debt and ensuring financial stability after graduation.
How do US students typically finance their education?
US students finance their education through a combination of sources. This includes federal and private student loans, which can cover a significant portion of tuition and fees. Scholarships and grants, which do not require repayment, are also widely used to reduce costs. Additionally, students may use personal savings, work-study programs, and part-time employment to support their education.
Can an education loan for a student save the tax of a parent?
Yes, an education loan can provide tax benefits for parents under certain conditions. In many countries, including the U.S., parents can claim tax deductions on the interest paid on qualified education loans. This deduction can reduce their taxable income, potentially leading to lower tax liability. However, the specifics vary by country and individual circumstances, so it’s advisable to consult a tax professional for precise guidance.
How much student loans are in the US right now?
As of 2024, U.S. student finance loan debt has surpassed $1.8 trillion. This staggering amount reflects the growing burden on borrowers, with the average student loan debt per borrower reaching approximately $37,000. Despite various relief measures and repayment plans, student loan debt continues to be a significant issue affecting millions of Americans.
What is the interest rate on student loans in the US?
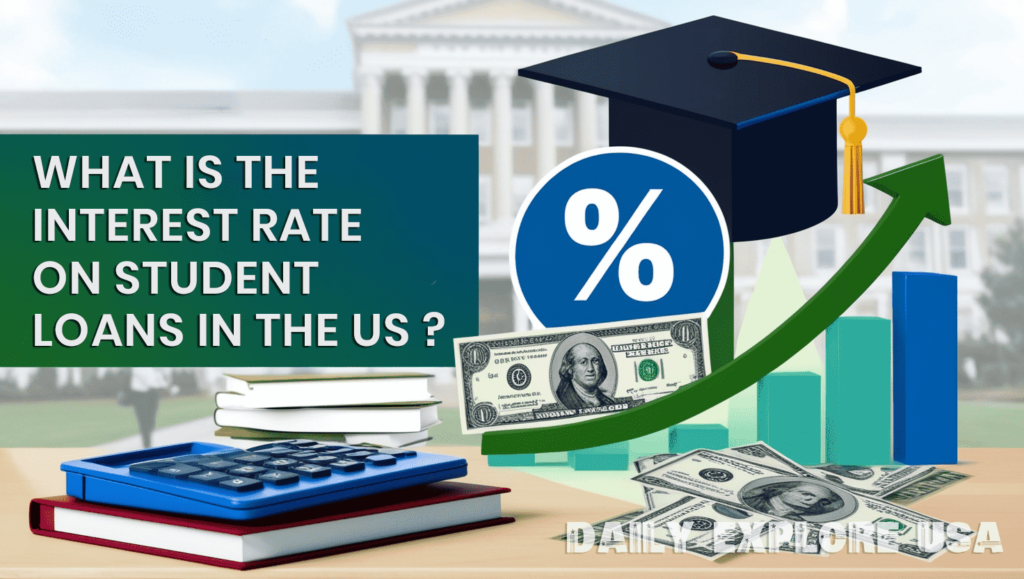
As of the 2024-2025 academic year, federal student finance loan interest rates for undergraduates are 5.50%, while graduate student loans are at 7.05%. PLUS loans, which are available to parents and graduate students, have an interest rate of 8.05%. The federal government sets these rates, which can vary annually based on the 10-year Treasury note. For private loans, rates can vary widely depending on the lender and the borrower’s credit profile.
How does the income-based U.S. Dept. of Education loan really work?
Income-based repayment (IBR) plans for U.S. Department of Education loans adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size. Under IBR, fees are generally capped at 10-15% of your discretionary income, and any remaining balance is forgiven after 20-25 years of qualifying payments. This plan helps make student loan payments more manageable if you have a lower income or face financial hardship.
How do private educational loans work in the USA?

Private educational loans in the USA are offered by private lenders, such as banks and credit unions, rather than the federal government. They typically have variable or fixed interest rates, and terms can vary widely between lenders. Approval often depends on the borrower’s credit score and income, and co-signers may be required for students with limited credit history. Unlike federal loans, private loans don’t always offer flexible repayment options or income-driven repayment plans. For more details, please visit the website.
How much is the average student loan debt for a graduate of a private university in the United States?
As of 2024, the average student finance loan debt for graduates of private universities in the United States is approximately $36,000 to $40,000. This figure can vary widely depending on the institution, program, and individual financial circumstances. Private universities generally have higher tuition costs compared to public institutions, contributing to the increased debt levels.
What is the percentage of students in the US who pay off their student loan debt after graduating from college/university?
Is this percentage increasing, decreasing, or staying steady over time?
What factors contribute to this trend?
As of recent data, approximately 30% of U.S. college graduates pay off their student finance loan debt within ten years of graduation. This percentage has been generally steady or decreasing over time due to rising tuition costs and increasing student loan balances. Factors contributing to this trend include higher education costs, wage stagnation, and economic fluctuations that affect borrowers’ ability to repay.
Where does the money used for student loans come from?
The money used for student loans comes from two main sources: the federal government and private lenders. Federal student loans are funded by the U.S. Department of Education through the Treasury, using taxpayer dollars, and are offered at fixed interest rates. Private student loans, on the other hand, are issued by banks, credit unions, or other private financial institutions, and their interest rates vary based on the borrower’s creditworthiness. Both sources provide funds to students for tuition and related educational expenses.
How long did it take you to pay off student loans?
What is your best advice?
I don’t have personal experience, but paying off student finance loans can take several years. My advice is to create a detailed budget, make extra payments when possible, and explore options like refinancing if you can secure a lower interest rate. Stay disciplined and proactive in managing your loan repayments.
In conclusion, student finance typically provides up to $10,000 annually for tuition, along with extra funds for living expenses and educational materials. This comprehensive support aims to reduce the financial load on students, making higher education more possible. However, the exact amount and coverage can vary depending on the program and individual needs, ensuring that a range of financial support options are available to accommodate different possibilities. If you want to learn more articles on topics you are interested in, you can visit our website. https://dailyexploreusa.com/